Door 21 – Non-terrestrial Networks (NTN)
Non-terrestrial Networks (NTN) – Satellite-Based IoT for remote regions
Global Connectivity with NTN
Conventional wireless networks are reaching their coverage limits. While LTE reaches about 90% of the global population, it covers only 15% of the Earth’s surface. Even with 2G and 3G, coverage rises to just 30–35%. As 2G networks are phased out, many remote regions risk losing connectivity altogether.
Non-terrestrial networks (NTN) are designed to close this gap. By transmitting data directly via satellites, NTN bypasses traditional radio masts and extends IoT connectivity to even the most remote areas.
How NTN Works
NTN refers to radio communication systems operating above the Earth’s surface. This includes satellites in low (LEO), medium (MEO), and geostationary (GEO) orbits, as well as high-altitude platforms and drones. Together, they provide seamless coverage where terrestrial networks cannot reach. Today, satellite communication often requires additional hardware. In the future, however, NTN will be integrated into the 3GPP ecosystem, allowing devices to switch seamlessly between terrestrial and satellite networks without extra equipment. If a terrestrial connection fails, NTN ensures uninterrupted service—critical for industries such as agriculture, forestry, logistics, and energy.
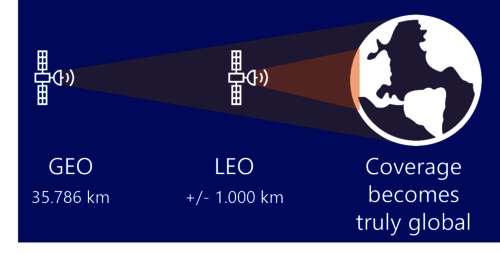
GEO vs. LEO Satellites
NTN employs both GEO and LEO satellites, each suited to different applications:
- GEO (Geostationary Orbit): Stationary at 36,000 km altitude, always accessible over the same region of the Earth. High latency and low data rate (2 – 4 kbps)
- LEO (Low Earth Orbit): Orbiting at 600–800 km, offering higher data rates (20 – 40 kbps), lower latency and lower energy consumption
Frequency and Device Integration
NTN uses two main frequency bands: n255 (1.6 GHz, L-band) and n256 (2 GHz, S-band). These overlap with terrestrial cellular bands, simplifying antenna design.
Modern IoT modules, such as Nordic Semiconductor’s nRF9151, already support both terrestrial and satellite communication. This compact system-in-package integrates LTE-M/NB-IoT, DECT NR+, GNSS positioning, and security features. Since mid-2025, firmware updates have enabled full NTN functionality, including GEO and LEO support. Nordic partners with providers like Iridium, Skylo, and Myriota to deliver global NTN solutions, with more vendors joining soon.
Outlook
As 2G and 3G networks disappear and demand for global IoT connectivity grows, NTN is emerging as a key technology for the future of networking. By combining modern satellite infrastructure with energy-efficient modules, NTN opens new business opportunities and makes previously inaccessible regions part of the connected world.
Participate and Win!
How does the competition work?
You can win a Chipolo LOOP or CARD and a Nordic DevKit of your choice on behalf of your company.
To enter, select which Chipolo finder you would like to receive, as well as which Nordic boards you would like to win (you can select multiple options, and the lottery will decide which one you may win).
Fill out the form now and, with a little luck, you will receive the combination of your wishes:
Registration Form
Unfortunately, the competition has now ended. Discover the products in our shop and get in touch with our Nordic experts.
Learn more about the prizes
Nordic Semiconductor is a global leader of ultra-low-power wireless technologies and a long term partner of Rutronik and is offering you the opportunity to win one of their development hardware. Participate in our advent calendar and explore the world of Power Management, Short Range, Wi-Fi and Cellular.
nRF54L15-DK
nPM1304-EK
nPM1300-EK
nPM2100-EK
Power Profiler Kit 2
nRF9151-DK
Thingy:91 X
The Nordic Thingy:91 X is a battery-operated prototyping platform for cellular IoT based on the nRF9151 System-in-Package (SiP) supporting LTE-M, NB-IoT, GNSS and NR+, and certified for global operation. It is the ideal platform for rapidly developing a prototype for any cellular IoT concept, and is especially suited for asset-tracking applications. Nordic Thingy:91 X enables location tracking using cellular (MCELL and SCELL), Wi-Fi, or GNSS, in combination with nRF Cloud Location Services.

On top of this you have the chance to win a finder from our customer Chipolo. This product is a lightweight, water-resistant item finder designed to help you find your missing valuable items.
Chipolo LOOP
Rechargeable tracker with flexible silicone strap for easy attachment. Enjoy the freedom of universal compatibility with Apple “Find My” or Google “Find My Device.”
Chipolo CARD
Thin, rechargeable tracker that fits perfectly in your wallet. Discreetly slim yet impressively loud, CARD helps you keep track of your most important flat items. Universally compatible with Apple's “Find My” or Google's “Find My Device”.